Is Centrosome Found In Plant Or Animal Cells
This folio content
one. Purpouse
ii. Synchronization
three. Duplication
4. Mitotic spindle
5. Cytokinesis
vi. Supernumerary
Centrosome is a MTOC (microtubule organizing middle) found in fauna cells, in both interphase and M stage. It is composed of a pair of centrioles and a surrounding pericentriolar cloth. A right cell cycle may depend on proper centrosomal action. More than 100 proteins forming function of the pericentriolar fabric, either permanently or transiently, are thought to participate in the jail cell cycle progression. The composition of the pericentriolar textile changes during the cell cycle, determining the part of the centrosome in each cell cycle phase.
During G1 of the cell cycle, or during G0, creature cells contain one centrosome. Notwithstanding, when cells pass the G1/South restriction point, Due south stage begins, and it leads to both DNA replication and to centrosome replication.
ane. Why two centrosomes?
During cell division, each of the two sister chromatids of every chromosome separates and go to 1 of the two new daughters. Otherwise, cells may become wrong number of chromosomes (aneuploidy), which ways that a cell may lack some genes or miss-regulates gene expression with potential dangerous consequences like prison cell inviability or becoming a cancer jail cell. A correct chromatids segregation depends on the proper germination of the mitotic spindle, a microtubule scaffold that are nucleated from ii centrosomes. The ii centrosomes are the mitotic spindle poles. During S phase of the jail cell cycle, the centrosoma is duplicated, and during G2 phase the 2 centrosomes move autonomously from each other to exist at distant locations in the cytoplasm. During 1000 stage, each centrosome nucleates microtubules of the mitotic spindle, which is bipolar. After cytokinesis, each daughter prison cell keeps a centrosome. Thus, like the DNA, centrosome has to exist duplicated in one case and only once during each partition.
ii. Centrosome and Dna duplication are synchronized
Dentrosome duplication and changes in their beliefs are synchronized with other candy happening along the cell wheel (Figure 1). CDKs (cyclin-dependent kinases) are phosphorylating enzymes responsible for catastrophe G1 phase and starting Due south phase. In the pericentriolar material of the centrosome, CDK1/Cyclin B is firstly activated for offset the S stage. In addition, centrosome duplication shares molecular regulators with Dna replication. For instance, both depend on CDK2/Cyclin E activity. In both, the centrosome and within the nucleus, in that location are molecules that are phosphorylated by these kinases and therefore they are activated at the same time, leading to Dna replication and centrosome duplication at the same time. Other mechanisms, like the increment in calcium concentration at the beginning of the S phase, may synchronize the activation of enzymes in both the cyotosol (centrosomes) and within the nucleus (Deoxyribonucleic acid).
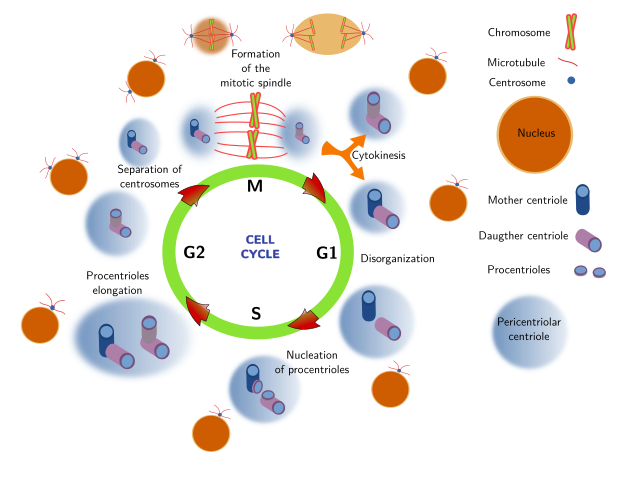
Effigy 1. Centrosome behavior during cell bike. During G1 phase, centrioles get disorganized and loose the orthogonal disposition. Offset the S phase, two new procentrioles nucleate from the two preexistent centrioles. At the finish of S phase, procentrioles increase their length. In G2 phase, there is an increment in the pericentriolar material (not depicted). At the end of G2 stage, each centrosome migrates to contrary places on the nuclear envelope. During K phase, the mitotic spindle is nucleated from the two centrosomes and sister chromatids are segregated betwixt the ii daughter cells. After cytokinesis, each girl cell contains one centrosome, and the cell wheel may start again.
iii. Centrosome duplication
Centrosome duplication depends on centrioles duplication (Effigy ii). Every centrosome contains a pair of centrioles before entering in S phase, female parent and daughter centriole. Fibrous proteins link both centrioles and keep them together. Mother and girl centriole duplication starts at the commencement of Southward phase. Procentrioles are the new nucleated centrioles, which elongate at the terminate of the S stage to reach a proper length. It is of notice that a procentriole takes a consummate cell cycle and a half to get a mother centriole, which bears distal and subdistal appendages.
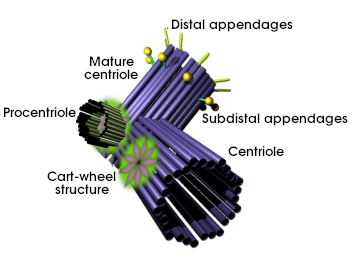
Figure 2. Centriole duplication involves a set of protein that form a cart-cycle similar construction close to the proximal cease of each centriole (mature: mother; centriole: girl). From this structure, triplet microtubules nucleate to form the procentriole. The centriole duplication starts at the commencement of the S phase.
During mitosis, centrioles of a centrosome are orthogonaly arranged, but this disposition changes in late mitosis or afterward mitosis. Separation of centrioles from each other happens past the activity of several proteins like Plk1. So, other proteins like rootelin and Nap1 make the connection between the proximal ends of both centrioles. This linking lasts untill G2/Yard transition (Figure three). Rootelin is also present in the proximal end of basal bodies.
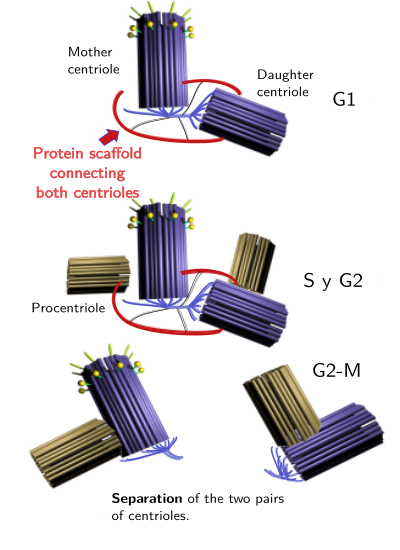
Figure 3. Both centrioles are linked by a protein scaffold. Durin G2/K transition, the intercentriole binding is disorganized and centrioles may travel to distant places of the cytoplasm, taking with them half of the pericentriolar material (adapted from Azimzadeh y Bornens, 2007).
The two centrioles, carrying their ain procentriole and a portion of the pericentriolar material, separate from each other in G2 (Figure three). The movement is driven by the activity of Eg5 kinesin, a microtubule associated motor poly peptide. Centriole separation requires breaking the connector fibers that kept the two centrioles together during G1 and Due south phases, and it ends upwards with 2 new centrosomes in the cell. G2/M transition leads to a maturation menstruum of the 2 new centrosomes. Earlier mitosis, centrosomes recruit more pericentriolar textile changing its molecular composition. For example, gamma-tubulin rings increase in number ascension the number of microtubule nucleation sites. Information technology was thought that pericentriolar material was baggy cloth, that is, information technology does not bear witness any organization. However, it is organized in layers showing torus-like structures (a shape like to donuts). It is also useful dividing the pericentriolar material in ii types of molecules: those permanently associated with centrioles, similar pericentrin and Plk4, and those recruited transiently like gamma-tubulin.
4. Mitotic spindle
Chiliaditotic spindle is built during the K phase of cell bike. Spindle microtubules nucleate in the pericentriolar material of the ii centrosomes. There are kinetocoric microtubules contacting with chromosomes, interpolar microbules contacting between each other, and astral microtubules with the plus ends toward the jail cell periphery. Chromosomes are non passive players, since they are involved in the germination and stabilization of microtubules. The position of centrosomes and the interaction of spindle microtubules with other prison cell components influence the orientation of the mitotic spindle, and therefore to place the division plane. The sectionalization plane is fix perpendicular to the long axis of the mitotic spindle and at the aforementioned distance from the two centrosomes (Figure 4). Location and orientation of the division plane determine the distribution of the cell components between the ii girl cells.
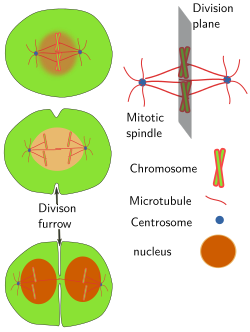
Figure 4. The position of centrosomes determine the orientation of the mitotic spindle and the partition plane.
Westhether centrosomes are essential for the formation of the mitotic spindle or not is not clear yet. When centrioles are removed by very precise laser irradiation, animal cells tin can still build a mitotic spindle cheers to chromosomes and microtubule motor proteins, although there is no cytokinesis or it is lacking. There are no centrosomes in establish cells, only they make perfect mitotic spindles and conduct out consummate cytokinesis (by dissimilar mechanism than in animal cells). Centrosomes practice not announced to be indispensable for the mitotic spindle formation in animal cells. However, when they are present, centrosomesare the principal responsible for the mitotic spindle formation, and they are necessary for a correct prison cell partition.
5. Cytokinesis.
One of the most important roles of centrosomes during cytokinesis is to establish the place where the division plane is going to have place. This plane is always perpendicular to the mitotic spindle and therefore depends on the initial position of the two centrosomes. No centrosomes or more than two centrosomes usually lead to a incorrect position of the partitioning plane. The right position is essential for asymmetrical divisions, which cease up with ii daughter cells having unequal amount of mother cell components. Thus, the two daughter cells may have dissimilar fates, both functionally and morphologicaly. For case, asymmetrical divisions are essential during female meiosis, early embryo development, many cell differentiation processes, maintaining a pool of adult stalk cells, and many others. An animal is not feasible without asymmetrical divisions.
During cytokinesis in some creature cells, like human cells, the mature centriole travels to the region where partitioning furrow is going to be finally airtight, and this movement happens at the same time as the two daughter cytoplasms become separated. Centrosome besides appears to be of import for regulating the vesicular trafficking during cytokinesis.
6. Supernumerary centrosomes
Although at that place are some cells containing more than 2 centrosomes, like muscle cells and hepatocytes during prison cell differentiation, having two centrosomes is very convenient for the formation of the mitotic spindle with ii spindle poles for a right chromosome segregation. Actually, more than 2 centrosomes in a cell is known as supernumerary centrosomes and information technology is frequently indicative of a cell flaw. Supernumerary centrosomes are frequent in cancer cell, and then that it was thought that centrosomes were responsible for chromosome disturbances because they can build multipolar mitotic spindles and therefore an diff segregation of chromosomes between the two daughter cells. All the same, information technology is not clear if supernumerary centrosomes are cause or upshot during cancer progression. Some cells tin can exercise correct mitosis with supernumerary centrosomes past concentrating centrosomes in two groups, one at each spindle pole, which is mediated by microtubule motor proteins and actin filaments. Then, why the number of centrosomes is so tightly controlled in beast cells? As nosotros said above, information technology looks like that the partitioning airplane orientation and asymmetric divisions are highly influenced past the position of the mitotic spindle, which depends on the position of the two centrosomes, and these two features are essential for animals.
Bibliography
Acilan C, Saunder WS. A tale of besides many centrosomes. Cell. 2008. 134:572-575.
Azimzadeh J, Bornens M. Structure and duplication of the centrosome. Journal of cell scientific discipline. 2007. 120:2139-2142.
Bettencourt-Dias M, Glover DM. Centrosome biogenesis and function: centrosomics brings new understanding. Nature reviews in molecular and prison cell biology. 2007. eight:451-463.
Bornens M. Organelle positioning and jail cell polarity. Nature reviews in molecular and cell biological science. 2007. ix:874-886.
Bornens M. The centrosome in cells and organisms. Science. 2012. 335: 422-426.
Fu J, Hagan IM, Glover DM . The centrosome and its duplication cycle. Cold Spring Harbour perspectives in biological science. 2015. vii: a015800.
Marshall WF. What is the function of centrioles? Periodical of cell biochemistry. 2007. 100:916-922.
Source: https://mmegias.webs.uvigo.es/02-english/5-celulas/ampliaciones/8-centrosoma-ciclo.php
Posted by: shotwellenbraing.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is Centrosome Found In Plant Or Animal Cells"
Post a Comment